Why do we have hair?
Let's explore the structure of hair follicles and hair to understand more about hair.
Wouldn’t it have been better if humans had fur all over their bodies like lions or were completely smooth without any hair like snakes?
Why do we have hair?
Let's explore the structure of hair follicles and hair to understand more about hair.
Wouldn’t it have been better if humans had fur all over their bodies like lions or were completely smooth without any hair like snakes?
Three hypotheses
Skin Parasite Theory

To proactively respond to climate changes

For sexual attraction
Hair, as a supplementary part of the skin, serves functions such as maintaining body temperature, adapting to changes in external climatic conditions, blocking ultraviolet rays, protecting our body from dust, sweat, raindrops, and even emitting sexual attraction. Therefore, these hypotheses about its functions likely emerged.
The structure of hair follicles and hair
The skin can be divided into epidermal and dermal tissues. The hair follicle is embedded in the dermal tissue, and the sebaceous gland is connected to it as shown in the diagram. The hair follicle consists of hair papilla cells that supply nutrients and oxygen to the root of the hair, matrix cells, melanin cells that produce color, and keratin cells that make up the hair itself.

Hair Follicle: The root where the hair grows
Sebaceous Gland: Provides sebum to the hair
Hair Papilla: Located at the very bottom of the hair follicle, composed of connective tissue and capillaries
Hair Matrix: Cells in the hair matrix divide and eventually form the hair strand; connected to the papilla below and receives nutrients from the capillaries
Blood Vessel: Arteries, veins, capillaries
Hair Follicle: The root where the hair grows
Sebaceous Gland: Provides sebum to the hair
Hair Papilla: Located at the very bottom of the hair follicle, composed of connective tissue and capillaries
Hair Matrix: Cells in the hair matrix divide and eventually form the hair strand; connected to the papilla below and receives nutrients from the capillaries
Blood Vessel: Arteries, veins, capillaries

The structure of hair follicles and hair
The skin can be divided into epidermal and dermal tissues. The hair follicle is embedded in the dermal tissue, and the sebaceous gland is connected to it as shown in the diagram. The hair follicle consists of hair papilla cells that supply nutrients and oxygen to the root of the hair, matrix cells, melanin cells that produce color, and keratin cells that make up the hair itself.

Hair Follicle: The root where the hair grows
Sebaceous Gland: Provides sebum to the hair
Hair Papilla: Located at the very bottom of the hair follicle, composed of connective tissue and capillaries
Hair Matrix: Cells in the hair matrix divide and eventually form the hair strand; connected to the papilla below and receives nutrients from the capillaries
Blood Vessel: Arteries, veins, capillaries
The Lifecycle of Hair
The Lifecycle of Hair
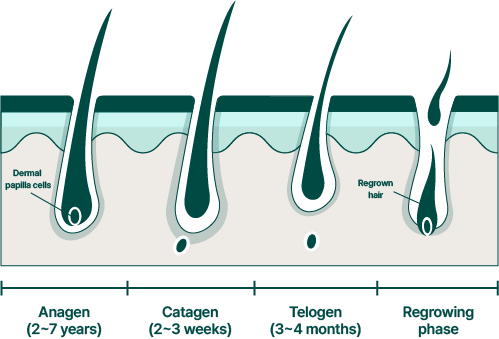
Typically, hair has a lifespan of 3-5 years and goes through three phases: Growth phase (Anagen, 2-8 years), Regression phase (Catagen, 2-4 weeks), and Resting phase (Telogen, 3-4 months).

Anagen
- This is the phase where the hair actively grows, with an average monthly growth of 1cm.
- Over 90% of hairs are in this phase at any given time.
- The average duration of the growth phase lasts between 2 to 8 years.
Catagen
- Connected to the end of the growth phase, the metabolic processes gradually decrease in this phase, and keratinization begins.
- Hair typically remains in this stage for around 2 to 4 weeks.
Telogen
- In this phase, the hair papilla shrinks, and the follicle reduces in size.
- Approximately 10% of hairs are in this phase. This stage typically lasts about 3-4 months, and it’s normal for 40-70 hairs to shed daily during this phase.
- If one starts to lose more than 100 hairs a day, it may be indicative of hair loss.
Return to Anagen
Return to Anagen
- New hair cell division gradually begins from stem cells located in the basal layer of the hair follicle.