The Connection Between Gut Health and Hair Loss: How Are They Related?
It's surprising to learn that gut health can influence hair loss, isn't it? Let's explore how gut health affects hair loss.
All organs in our body are closely connected, and the gut, in particular, is a key organ responsible for overall health. Recent studies have revealed that gut health also impacts hair loss.
How are gut health and hair loss connected?
Gut Microbiome Imbalance: The gut microbiome plays a role in various physiological functions, including the immune system and digestion. An imbalance in gut bacteria can lead to conditions like leaky gut syndrome or inflammation. Increased inflammation can affect hair follicles, hindering hair growth. Inflammatory cytokines, substances that contribute to inflammation, can weaken hair follicles, leading to hair loss. Additionally, Studies have that the gut bacteria composition in hair loss patients differs from that of healthy individuals. Nutrient Malabsorption: Poor gut health can lead to nutrient malabsorption. If the body doesn't properly absorb essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and amino acids, which are crucial for hair health, hair may become weak, resulting in hair loss. For instance, deficiencies in iron and vitamin D can accelerate hair loss. Since these nutrients are absorbed in the gut, so if gut health is compromised, the body may not receive adequate amounts of them. Hormonal Imbalance: Gut health influences hormonal balance. The gut microbiome is involved in the metabolism of hormones such as estrogen, and when gut function declines, hormonal imbalances can occur. In women, hormonal imbalances can exacerbate hair loss. For example, conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can lead to hormonal imbalances, which may contribute to hair loss. Nervous System Influence: The "gut-brain axis" theory suggests that gut microbiota influences the brain through signaling pathways. Since the gut and brain are closely linked, gut health can affect brain health. Stress is one of the main causes of hair loss, and poor gut health may make the body more vulnerable to stress, which can worsen hair loss.
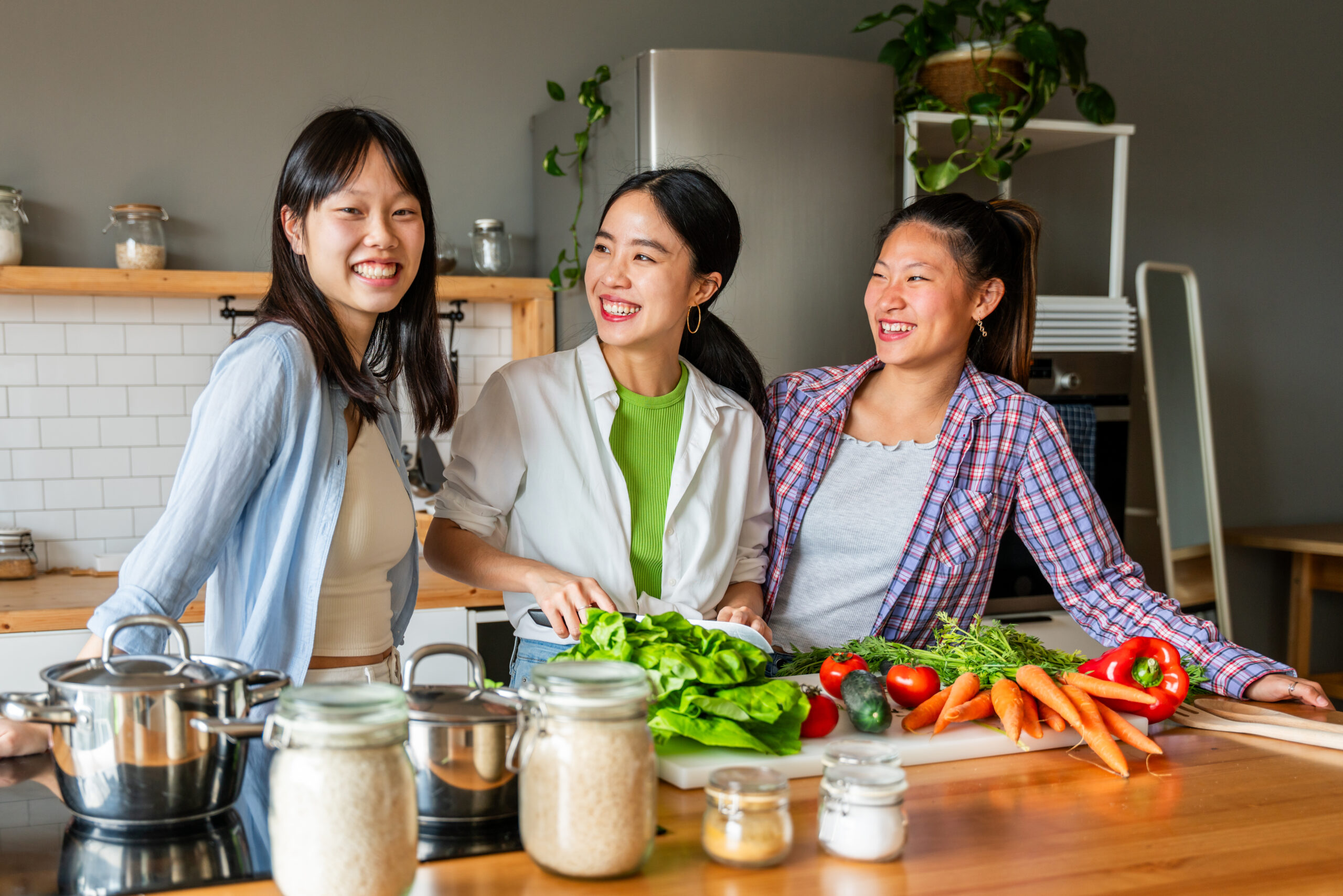

Can Efforts to Improve Gut Health Help Prevent Hair Loss?
Probiotics: Consuming probiotics, such as beneficial gut bacteria like lactic acid bacteria, can improve the gut environment. Fiber: Fiber is essential for gut health and serves as food for beneficial gut bacteria, promoting a healthy gut. Fermented Foods: Fermented foods like kimchi and yogurt, which are rich in probiotics, can support gut health. Limit Refined Carbohydrates: Refined carbohydrates can promote the growth of harmful gut bacteria, damaging gut health. Stress Management: Since stress negatively impacts gut health, managing stress is important. In conclusion, while research on the link between gut health and hair loss is still in its early stages, there is growing evidence that maintaining a healthy gut can play a role in preventing hair loss. Efforts to maintain gut health, such as a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and stress management, may help prevent and improve hair loss.